When it comes to citrus, most of us are left with the impression that we've swallowed something whole, tasted a little of it, and sometimes just for the simple purpose of filling or relaxing! When you think about it, the person who savors it will pay attention to its appearance and internal taste. This is what we call fruit quality. Fruit quality is divided into two aspects of sensory properties and biochemical properties and sensory properties by the people through sight, smell, touch, taste, give a person a kind of knowledge, including the appearance quality of the fruit size (longitudinal diameter x transverse diameter), skin thickness, shape, color, surface defects (such as wind damage, wear, rusty spot), and acid, sweet, bitter, astringent, chewing feeling when the fruit hardness, tender flesh, edible rate and melting rate, etc. Biochemical properties refer to the amount of nutrients and health functional substances contained in fruit, including fruit pigment, VC, amino acids and minerals.
People fruit symbolizes the harvest, the more influence factors in the process of production quality, including genetic factors (hybrid parent), external environmental conditions (climate, altitude, soil, etc.), cultivation management measures (irrigation, sewage sludge, pruning, collecting, stock, etc.), and the fruit packaging and transportation, this fruit is a complex system of agricultural engineering.
Through this paper, citrus fruit appreciation, combined with the actual planting management, farming operations and other analysis of fruit factors and regulatory mechanism.
Key words: citrus, fruit appreciation, action mechanism, influencing factors.
1. Citrus fruit appreciation index and its action mechanism.
Usually, we measure the fruit quality is judged by its taste, whether it is the farmer's market, hawkers, fruit shop to buy, usually have a taste of the sample, but not all the taste of people are consistent, different people have different preferences, some people like the meta-acid, some people like a sweet, even if the same fruit different people have different taste sensitivity. Therefore, to judge the quality of fruits, we should establish a quantifiable standard system of fruit appreciation. The following are the indicators and mechanism of fruit appreciation:
1. Sensory appreciation index
Appearance: fruit size (longitudinal diameter transverse diameter), smoothness of fruit surface (oil package size), fruit color.
Longitudinal diameter measuring
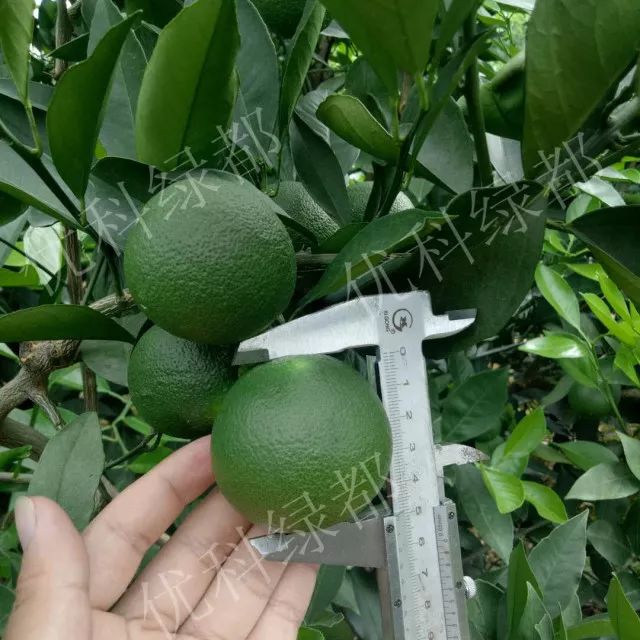


Transverse diameter measuring Orange red, oil cell smooth.
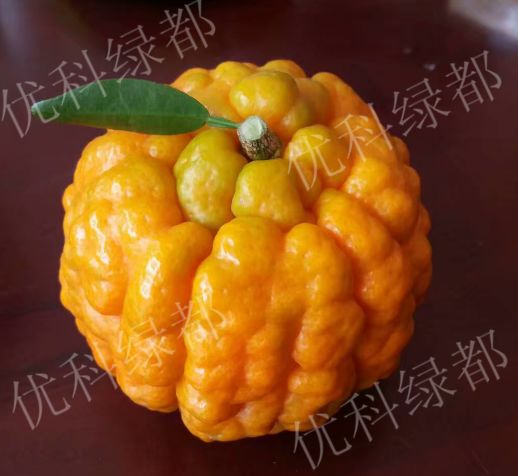

Orange yellow, oil cell is bulky.
Edible rate: the percentage of edible part and total.
(3) slag rate: after the entrance of the slag part and the percentage of edible part.
(4) soluble solid (sugar): mainly refers to the soluble sugar, including monosaccharide, disaccharide, polysaccharide (in addition to starch, cellulose, chitin, hemicellulose insoluble in water), commonly have glucose, fructose, maltose and sucrose, determination of soluble solid can measure the fruit maturity, in order to determine the time to pick.
(5) total sugar (glucose meter/sucrose) : namely the total soluble solids and total sugar of common refers to reducing glucose, fructose, pentose, lactose and under the condition of determination can be hydrolyzed to the reducing of monosaccharide sugar (hydrolyzed to glucose + 1 molecules fructose 1), malt sugar (glucose) hydrolysis of 2 molecules and may be partially hydrolyzed starch (glucose) hydrolysis of 2 molecules, in some sugar meter for total sugar contains soluble solids (such as glucose meter).
Total acid (citric acid meter) : the fruit contains a variety of organic acids, total acidity determination results are usually the most content of the kind of organic acid samples to calculate the results. The main organic acid composition of different fruits is different, and their conversion coefficient is also different, such as malic acid, the conversion coefficient is K=0.067, the main fruit is apple, pear, peach, apricot, plum, tomato, lettuce; Tartaric acid, the conversion coefficient is K=0.075, and the main fruit is grape; Citric acid, the reduction coefficient is K=0.070, and the fruit is citrus; The total acid of citrus fruits should be measured by citric acid titration. The formula for calculating the total acidity measured by laboratory fruit titration is as follows:
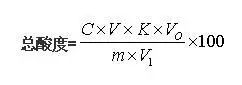
Where: concentration of c-standard NaOH solution, mol/L;
V- titration consumption standard NaOH solution volume, mL;
M - sample mass or volume, g or mL;
V0- total volume of sample diluent, mL;
V1- volume of sample liquid absorbed during titration, mL;
K minus the conversion factor, which is 1 mmol of NaOH is equal to the number of grams of the main acid.
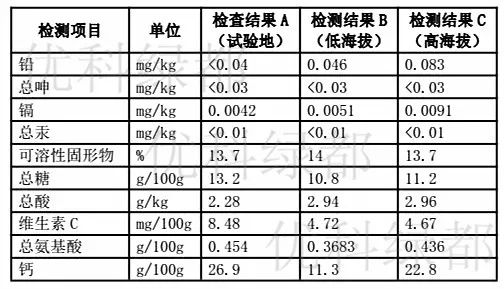
The detection report of citrus fruits in a base entering the turning stage is shown as the following figure:

The results were compared as follows:
The trend is as follows:
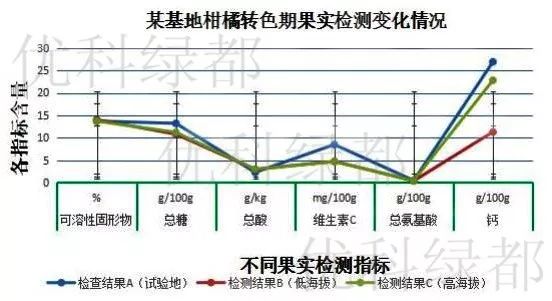
It can be seen from the figure that each index of fruit quality in the test plot (whole-process integration of water and fertilizer) is relatively better than that in the control group (low altitude and high altitude), especially the content of total sugar, vitamin C and total amino acid is obvious.
The test of a certain sugar and acid all-in-one machine is as follows:



Meaning of test value:
Brix% (sugar content) : represents the weight and percentage of sucrose in 100g sucrose solution. It measures the total soluble solids in the solution, namely the total sugar concentration.
Acid: the total Acid in the sample is tested according to the principle of conductivity and converted into citric Acid (citrus), tartaric Acid (grape) and malic Acid (apple) concentration.
1.1.1 mechanism of action of citrus fruit sugar and organic acids.
Citrus fruit sugar (sugar content) and organic acid (acidity) are important indicators for fruit quality and flavor judgment, and important basis for determining fruit classification, maturity, taste evaluation and commodity price, etc. Therefore, it is extremely important to understand the mechanism of the formation or accumulation of citrus fruit sugar and organic acid.
Citrus fruit sugar is mainly composed of leaf (source) leaves photosynthesis in leaves after the synthesis of assimilation product transportation to reach the fruit, fruit juice, the accumulation of soluble sugar in the cell is the vast majority of sucrose, glucose and fructose, and these three different sugar taste sweetness, the highest fructose sweetness, 1.73 times that of sucrose, 2.7 times that of glucose (sweetness: fructose > sucrose > glucose), scale for different kinds of sugar and fruit sweetness and flavor. The main form of citrus sugar transport is sucrose, which is synthesized in the cytoplasm, then entered the cytoplasm and stored in the vacuole. In general, the accumulation of sugar in fruits began at the stage of fruit expansion and mainly accumulated soluble sugar at maturity. In different citrus varieties, the accumulation of soluble sugar in the cytoplasm is different when the fruit is ripe. For example, the accumulation of sucrose is dominant in wide-skinned citrus, while the accumulation of hexoses (glucose + fructose) is dominant in sweet lime and summer orange.
The content of acid in citrus fruit has an important influence on the flavor, storage, transportation resistance and market acceptability of the fruit. According to the content of titrable acid, it can be divided into high-acid varieties (>1.5%), medium-acid varieties (0.5% -- 1.5%) and low-acid varieties (<0.5%). The source of organic acid accumulation in citrus fruits was different from that of sugar. At the mature stage, citric acid was the main organic acid in most citrus fruits, followed by malic acid and quinic acid, such as oranges (navel oranges, ponkan oranges, willow oranges, newhall navel oranges, etc.) and broad-skinned oranges (wenzhou mikan, ponkan, wo mandarin, huo mo huo, mercotte, aiyuan 38, granulated tangerine, etc.). Low-acid or acid-free juices are dominated by malic acid, such as sweet lemon and dark sweet orange.
1.2 biochemical evaluation indexes:
Fruit pigment: the color of citrus flowers and fruits is mainly determined by water-soluble pigment (flavonoids, beet pigment) and fat-soluble pigment (carotenoids, chlorophyll) :

Amino acids: fruit contains essential amino acids, semi-essential amino acids and non-essential amino acids, such as threonine, lysine, valine, phenylalanine, histidine, glutamate and so on.
VC: vitamin C, also known as l-ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin, lack of it can cause scurvy.
1.2.1 mechanism of action of major pigments in citrus fruits
When the citrus fruit is immature, it accumulates a lot of chlorophyll. The color of carotenoids is covered by chlorophyll, making the peel dark green and the flesh light green. After fruit is mature, chlorophyll is degraded, basically contain kind of flavonoid and carotenoid, make pericarp mostly show yellow, orange yellow or orange red, flesh shows orange yellow, flaxen or orange red. In most citrus skins and pulp, its orange yellow, orange red, pink or red is mainly caused by the large accumulation of carotenoids, while blood orange is the only orange strain mainly colored by anthocyanin.
Carotenoids can be synthesized and accumulated in green and non-green parts of plants. The carotenoids in carotenoids contain no oxygen atoms, and the molecular formula is C40H56. Xanthophyll contains two oxygen atoms, and the molecular formula is C40H56O2. Flavonoids are synthesized in the cytoplasm of plant cells through a series of enzymatic hydrolysis reactions on the main chain (chalcone synthase, chalcone isomerase, flavanone 3-hydroxylase, flavanone 4-reductase, etc.) to further form anthocyanin and anthocyanin. Anthocyanin or anthocyanin is the derivative of 2-phenylbenzobenzopyrane (), while anthocyanin is the sugar, acyl or methyl substituent of anthocyanin. The right phenyl ring hydroxyl substitution of anthocyanin is different, and anthocyanin can be divided into geranium pigment (brick red), centaurea pigment (purple red) and delphinidin.
2. Analysis of influencing factors of fruit quality
There are many factors affecting the quality of citrus fruits, such as variety characteristics (innate genetic factors), external factors (acquired growth environment), external factors such as growth environment, fertilizer and water management, farming operation, and post-harvest packaging and transportation, etc. To understand the factors affecting the quality of citrus fruits and to control them in time can ensure the best taste and flavor of citrus fruits when they are ripe, that is, to ensure the reasonable ratio of sugar and acid, the rate of slag melting, peeling and so on.
2.1 environmental factors
In the process of citrus growth, environmental factors should be the primary consideration, because the growing environment is mostly objective and uncontrollable. For example, local climate problems include altitude (latitude and longitude), annual rainfall, air temperature and humidity, duration of sunshine, temperature difference between day and night, soil type, light quality and so on.
Such as the influence of illumination on the accumulation of sugar in the bagged fruit mature period, the same trees, different parts of fruit by light intensity, general illumination intensity is abate, in turn in the canopy on the part of peripheral lighting quantity than cella light quantity is big, so outside the upper fruit and fruit are more mature than before, in order to guarantee with the number of fruit taste homogeneity, general batch picking first pick when the upper and the periphery of the fruit.
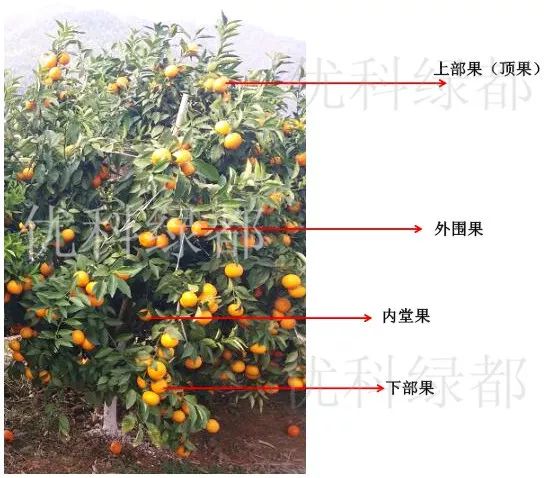

2.2 cultivation and management measures
(1) stock selection: general citrus stock selection has orange, orange, orange, orange, etc., different culture environment should choose different stocks for grafting. For example, if the water level in guangxi is high and the humidity is high, the fruit of aurantii is generally selected as the rootstock. In the characteristic areas of yunnan plateau, especially in mountainous areas with high winds and low water level, the anvil of orange is generally selected for grafting. Of course, other factors should be considered in the selection of grafting rootstock, such as the resistance to diseases and affinity of rootstock.

Product shell root stock
(2) fertilizer and water management: fertilizer and water management is the fruit sugar, organic acid, minerals, VC and amino acid accumulation of important factors, reasonable fertilizer formula, fertilization is the key to the normal supply of fruit nutrition.
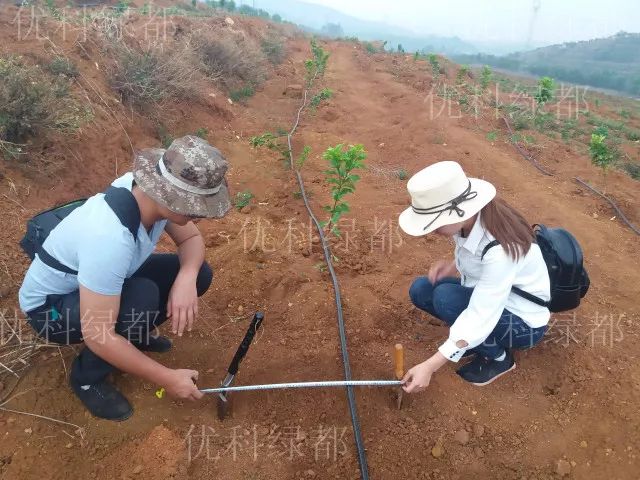


Soil penetration range measurement
(vertical penetration + horizontal penetration + deep penetration)
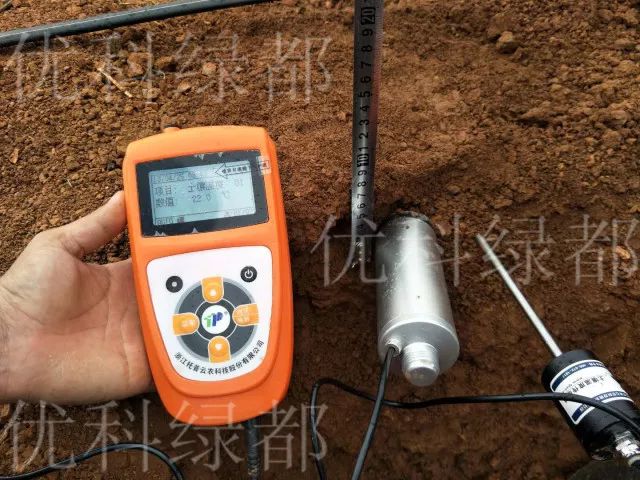

Soil temperature and humidity measurement
Through field measurement, the fertilization time and frequency can be accurately grasped, so that the fertilizer can quickly penetrate into the main distribution layer of root system through mass flow and diffusion, so as to ensure the efficient supply of water and nutrients to crops.
(3) trim
Personally, I think pruning is one of the most important farming operations in planting management, because the quality of pruning means the number of hanging fruit in the coming year (reasonable ratio of leaf to fruit), the location of hanging fruit, light and air permeability, fruit nutrition supply and so on.

Usual clip method has put tip of wipe bud, pick the heart, short cut, dredge cut, retractive cut. According to the orange tree is different, different growth period, the pruning way, combined with twenty-four seasonal (weather conditions) arrange clip, do reasonable Ye Guo than (walter spinosa plain 50:1 fruit, sweet orange plain 40:1 fruit), branches strewn at random have send, ventilation and pervious to light, avoid too much sun, unified put tip, mother GuaGuo branches and GuaGuo parts scheduled for next year.


2.3 harvest and preservation
From the planting terminal to the consumer's mouth, time difference and preservation measures can also lead to fruit quality deterioration. Fruits have self-ripening function in the process of transportation, so the picking side must be well controlled, and the proper picking period (maturity) and preservation measures (cold chain logistics, cling film, buffer plastic, etc.) should be selected to ensure the best fruit quality in the hands of different consumer groups.
